Forward Cloud Secure Edge (CSE) Events to the ELK Stack
Use our Filebeat integration to view and analyze CSE events in your ELK stack
- Overview
- Pre-requisites
- Steps
- Step 1: Create an API key in CSE’s Cloud Command Center
- Step 2: Store your API key secret in Filebeat
- Step 4: Verify Ingestion
- Next Steps
- Additional Info
Overview
Use this guide to forward Cloud Secure Edge (CSE) events into your ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) stack for centralized monitoring and troubleshooting. CSE emits detailed security and policy events through the CSE Events API. Using our Filebeat integration, you can:
- Collect events directly from the CSE API
- Forward events into Elasticsearch for indexing
- Visualize events in Kibana dashboards
Following the outlined steps, you’ll create an API key in CSE, configure Filebeat using the API key, and validate that CSE events appear in Kibana.
Pre-requisites
- CSE Admin account
- Filebeat server access with permissions to install keystores and edit
filebeat.yml - Access to Elasticsearch and Kibana
Steps
Step 1: Create an API key in CSE’s Cloud Command Center
1.1 In the Command Center, navigate from Settings > API Keys.
1.2 Add a new API Key and configure the following details:
- Name:
Filebeat Integration - Description: Used by Filebeat to collect events from CSE
- Scope:
ReadOnly
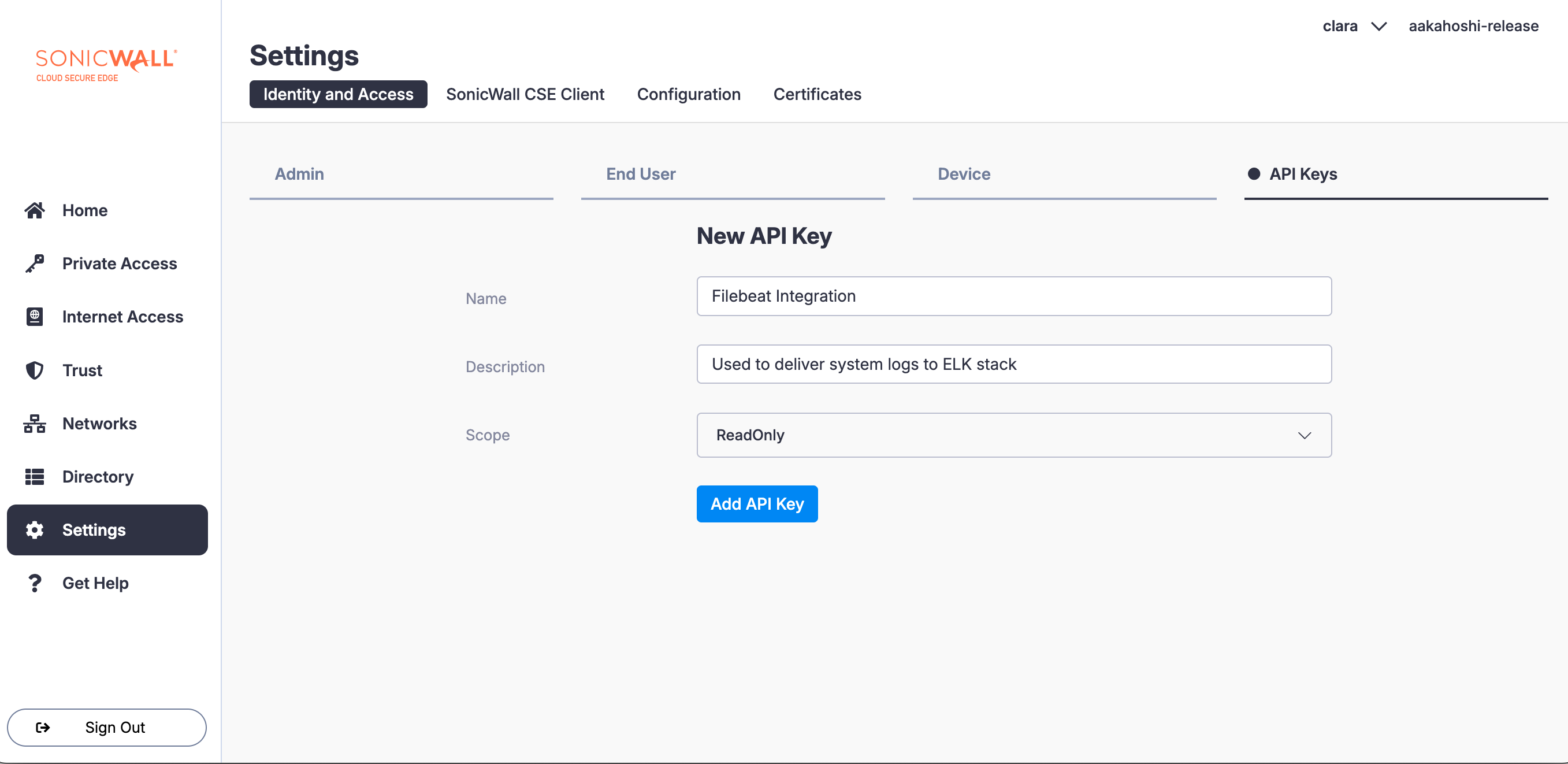
Copy and save the generated API Secret securely; you’ll use it in Step 2.
Step 2: Store your API key secret in Filebeat
Create the key store (if it doesn’t exist)
2.1 Log into your Filebeat server.
2.2 Run the following command in your CLI:
filebeat keystore create
Add the API key
2.3 Run the following command in your CLI:
filebeat keystore add <CSE_API_KEY> # Replace <CSE_API_KEY> with your API key name
Enter the saved API Secret
2.4 When prompted, paste the API key Secret (saved from Step 1) in the CLI.
Step 3: Configure Filebeat
3.1 Enter the following into the filebeat.inputs section:
- type: httpjson
config_version: 2
interval: 1m
request.url: 'https://net.banyanops.com/api/v1/events' # If using the European EUCC Command Center, then replace `net.banyanops.com` with `eucc.console.banyanops.com`.
request.transforms:
- set:
target: header.Authorization
value: 'Bearer ${CSE_API_KEY}' # Uses keystore variable
- append:
target: url.params.after
value: '[[ .cursor.last_created_at ]]'
default: '[[ (now (parseDuration "-5m")).UnixMilli ]]'
- append:
target: url.params.order
value: 'ASC'
- append:
target: url.params.severity
value: 'INFO'
- append:
target: url.params.limit
value: '1000'
response.split:
target: body.data
cursor:
last_created_at:
value: '[[ printf "%d" (add (toInt (index .last_event "created_at")) 1) ]]'
fields_under_root: true
fields:
event.dataset: cse
3.2 Save your changes.
3.3 Restart Filebeat:
sudo systemcl restart filebeat
Note: For more information on how to start Filebeat on each platform type, visit here.
Step 4: Verify Ingestion
4.1 Run a quick query in Elasticsearch to confirm events are flowing in:
curl -s "http://localhost:9200/filebeat-*/_search?q=event.dataset"cse&size=1&pretty"
4.2 In Kibana, search for event.dataset:cse to view and filter CSE events.
Next Steps
- Review the CSE Event Properties and Definitions for field definitions.
- Set up ELK alerts to notify when there are high-severity events.
Additional Info
The filebeat.yml file contains editable fields. Some of these fields are described below:
| Filebeat.yml Key Value Pair | Note |
|---|---|
type: httpjson |
Our API for event logs returns JSON format. |
interval: 1m |
We recommend setting the interval to once per minute to avoid exceeding the API rate limit. |
value: 'Bearer ${CSE_API_KEY} |
CSE_API_KEY is the Name of the key stored in Step 1. We recommend entering the key into a secure space (i.e., Filebeat keystore) rather than entering the plain text of the key in the filebeat.yaml file. |
value: '[[ .cursor.last_created_at ]]' |
Using our last_created_at value in the events JSON will provide the last time the events database consumed data. |
default: '[[ (now (parseDuration "-5m")).UnixMilli ]]' |
If the last_created_at field is unavailable (most often occurs during the first launch of integration), we recommend obtaining only the last 5 minutes of data, so that you don’t exceed the request size limit. |
event.dataset: cse |
We recommend calling the events something specific for easy searching and filtering (e.g., ‘cse’). |