Blocked access to websites when using Microsoft Edge and Risk-Based URL Filtering
End users receive 403 errors when attempting to access websites
Overview
When Microsoft Edge’s Internet Explorer (IE) mode and URL filtering are enabled in an org, select websites can be erroneously forced into ‘IE mode’ (e.g., outlook.live.com), blocking end users’ access to sites that should be accessible.
Symptoms
- End users receive a 403 error code (i.e.,
HTTP 403 Forbidden) when trying to access a modern website. - When Internet Threat Protection (ITP) is disabled, the website is not forced into IE mode and is therefore accessible.
Potential Root Cause(s)
There is an incompatibility between the modern website’s expectations of browser functionalities and IE mode; As a result, the website’s server refuses the connection with the browser and throws a 403 Forbidden error.
Microsoft Edge marks web pages that bypass PAC files (i.e., those listed on a global allow list, so that they bypass Risk-based URL filtering) as part of a Local Intranet zone, triggering IE mode. If an end user attempts to access a URL that exists on a global allow list, the URL will be erroneously forced into IE mode. Since the URL is actually a modern website path and not a legacy site, the website’s requirements are incompatible with the browser in IE mode, and this results in an error.
Resolution Steps
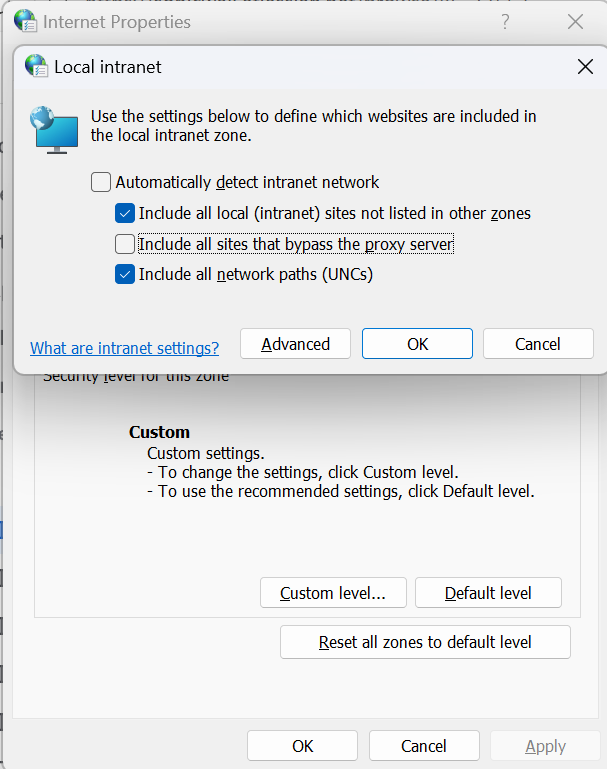
Disable Microsoft Edge from marking sites that bypass the PAC as Local Intranet zone sites:
-
From the Windows application panel, navigate from Internet Options > Security > (Select Local Intranet) > Sites.
-
De-select Include all sites that bypass the proxy server.