Datacenter Deployments
- Updated on May 16, 2024
Many IT organizations today have to manage distributed infrastructures that span multiple on-premises, data centers and cloud IaaS locations. Since Access Tiers can be deployed independent of the underlying network and managed via the Cloud Command Center, they can be used to simplify access controls management and improve security for even the most complex environments.
Multi-Region Datacenter
An organization may have office and datacenter locations that are spread across multiple geographies. A common deployment model is to have 1 Access Tier per location, similar to the Isolated VPCs deployment for IaaS.
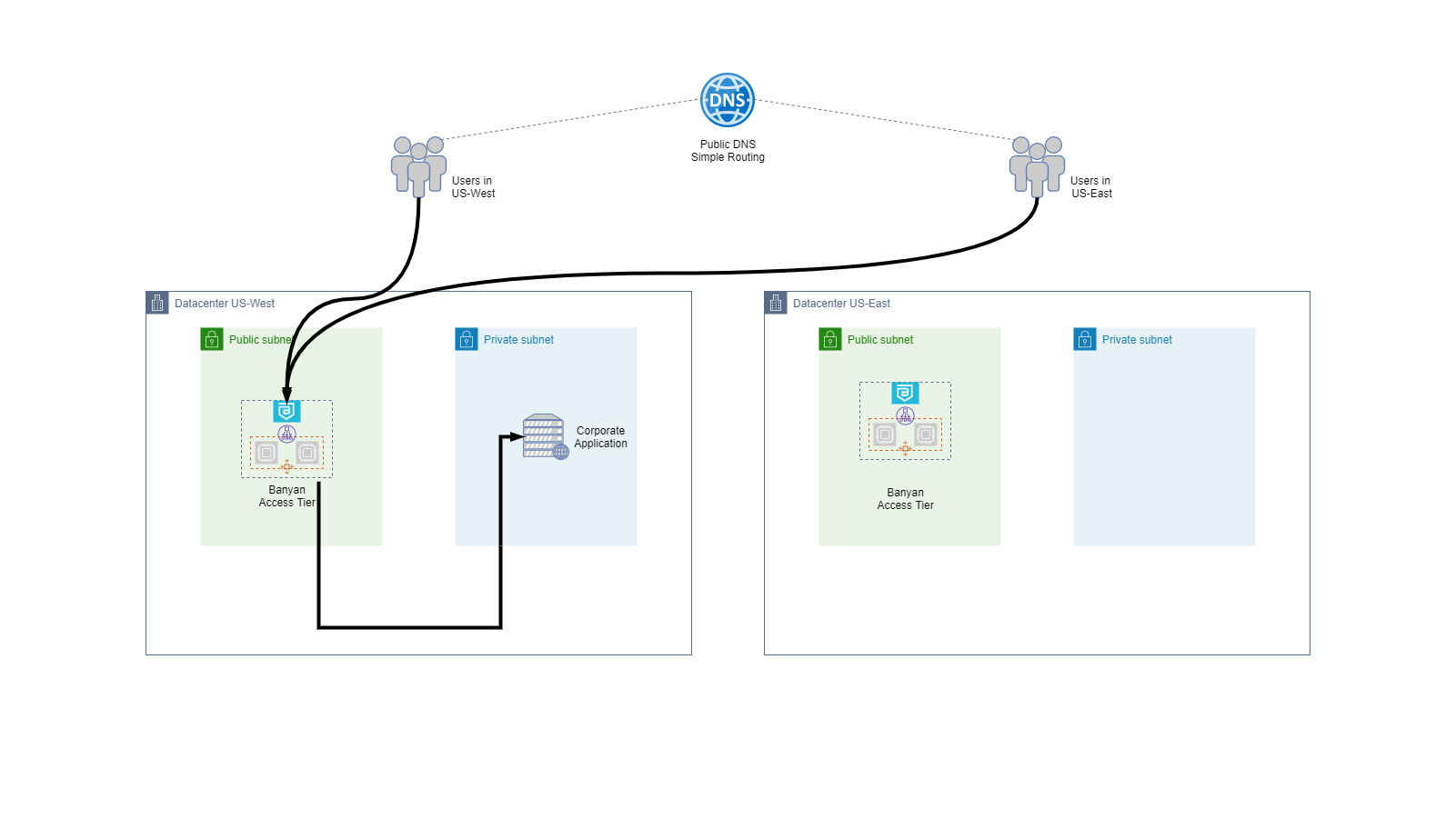
In an Multi-Region Datacenter deployment, we typically have:
- 1 Access Tier per location; each Access Tier is assigned a unique descriptive wildcard site domain name (such as
*.myapp.corp.example.com) that is used in the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for services in that location. You can create specific DNS entries for services that cannot follow this FQDN convention. - Individual locations are responsible for managing their Access Tiers and services. Administrative access and Policy/Role/Service management can be controlled and audited via Admin Profiles and Audit Logs API.
A key security benefit of this style of deployment is that we can eliminate almost all East-West lateral movement. Even if an attacker were to establish a foothold inside a location, they could not move laterally into another location.
Hybrid & Multi-Cloud
In more complex deployments that involve multi-cloud or datacenter-cloud connectivity, organizations often choose to use dedicated links - such as AWS DirectConnect or Azure ExpressRoute Gateway - to enable connectivity.
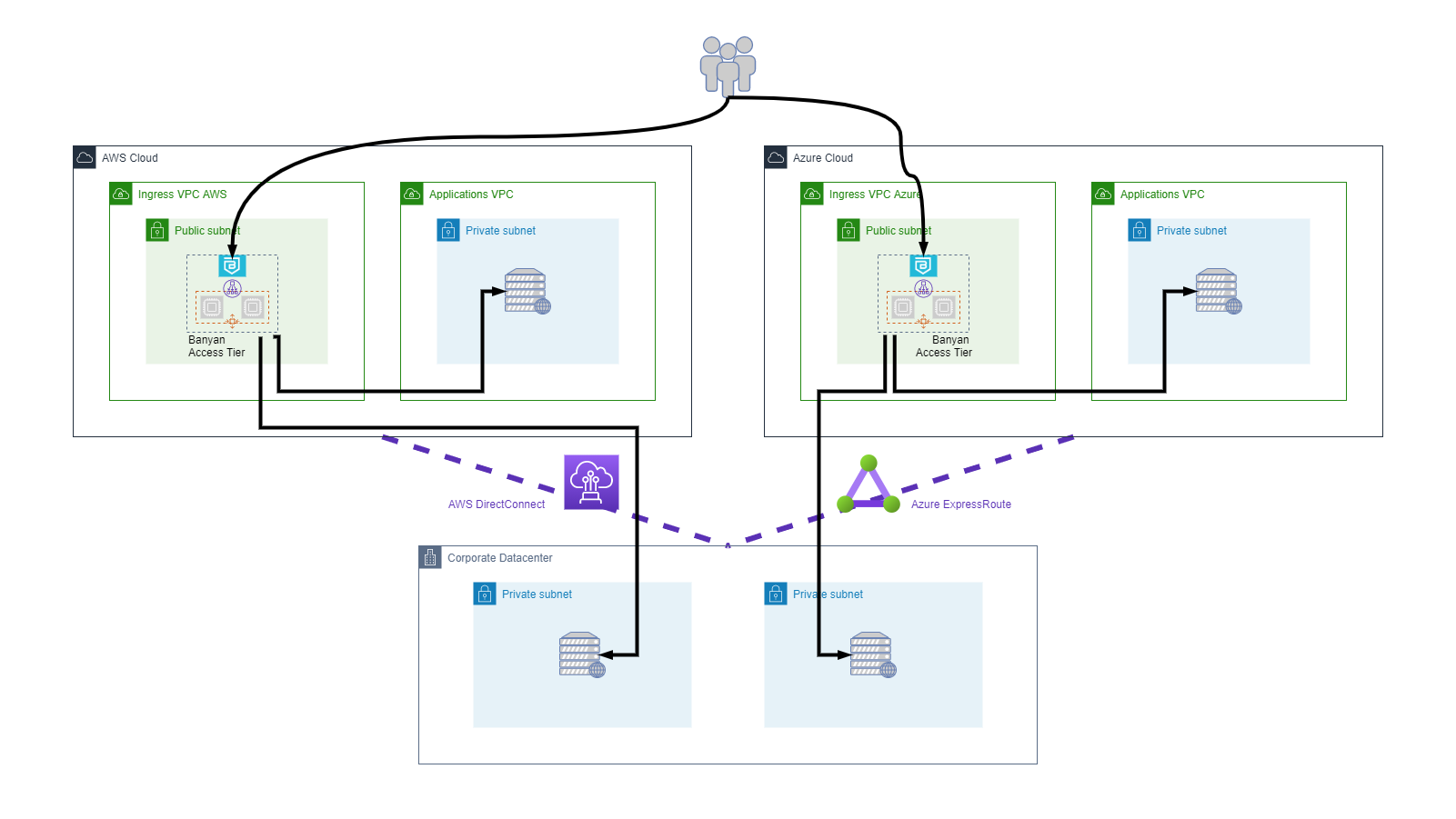
Access Tiers can be integrated seamlessly into these types of complex network topologies as well, because they run independent of the underlying network.